Dr Kiran Kumar Mukku, MD DM
14 April 2021
Stones not precious enough to cherish!!
Kidney stones are one of the most common kidney problems with which the patients approach a Nephrologist. Kidney stones are particularly common in the summer months because of the fact that people get dehydrated which in turn predisposes to stone formation. It is estimated that about 20% of men and 10% of women experience a kidney stone in their lifetimes till the age of 70 years. Men have higher propensity to form stones than women. Kidney stones can cause damage to the kidneys and may lead to permanent failure needing dialysis and transplant. So its important to note that kidney stones once detected needs thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment
What are kidney stones and what are the different types?
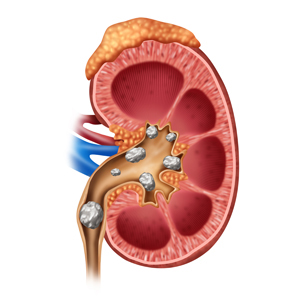
Kidney stones are lumps of minerals and salt substances which are formed when these minerals and salts are in high concentrations in the body and the amount of water in the body is less. Most of the kidney stones are composed of calcium oxalate (70-80%). Other stones are made of calcium phosphate, uric acid ,cysteine. Very rarely kidney stones are made of a combination of substances called Struvite stones composed of triple phosphate – Magnesium ammonium phosphate which is a very complex type of stone and may form very big sizes and may lead to kidney failure. Struvite stones are also formed when a patient is afflicted with urine infections due to a particular bacteria called Proteus vulgaris.
Why are kidney stones formed?
Kidney stones are formed when substances like calcium , oxalate, uric acid , cysteine stick together and form crystals and stones because there is not enough water in the urine to dissolve them. Some people are deficient in an enzyme that breaks down cysteine and hence this substance accumulates and forms stones. Some others don’t have enough citrate which blocks the formation of stones.
Am I likely to get kidney stones?
Its important to seek out the risk factors and cause of kidney stone formation and treat it to prevent recurrence. If you got kidney stones anytime before or any of your immediate family has kidney stones , you are likely to get them. If you don’t drink enough water or eat lots of salt , meat or sugar or if your are obese, you might be at high risk. Certain medical problems like diabetes mellitus, bowel diseases – Crohn’s disease , inflammatory bowel syndrome , gout – high uric acid levels , polycystic kidney disease, Renal tubular acidosis , Hyperparathyroidism – hyperfunctioning of parathyroid glands may predispose to formation of kidney stones. Some medications like antibiotics – ciprofloxacin and sulpha drugs , HIV medicines are also contributors to stone formation. Apart from all the above risk factors , specific surgeries likes weight loss surgery – Roux-en-Y gastric bypass operation also leads to oxalate stones.
What are the symptoms of kidney stones?
Many a times ,kidney stones cause back pain, below the ribs at the lower back. Sometimes this back pain can spread towards same side groin or lower belly and also scrotum in males. This pain can be worst pain in the life (as described) or mild dull ache. Its not related to any movements of the body. This pain comes in waves – episodic – comes and goes. Other symptoms like nausea, vomitings , fever can be present along with the pain. Blood in urine can happen if the stone injures the lining of the bladder or ureter. Burning while peeing can happen. Not uncommonly, some patients don’t experience any pain but present to doctors with a quite big stone that has caused significant damage to the kidneys. In case of stones in the bladder obstructing the urethral opening ( the opening through which the urine ultimately is flushed out) , patients may experience retention of urine where the urine doesn’t comes out despite having the urge to urinate. They also can have dribbling of urine or interrupted urinary stream due to ball valve mechanism where the stone gets stuck in the urethral opening.
How do I know if I have kidney stones?
The best imaging modality to detect kidney stones is plain CT Scan of kidney, ureter and bladder. CT Scan helps in detection of kidney stones , size of stones , exact location of stones in the urinary system. Since CT scan ia an expensive modality , X ray or Ultrasound are screening tools. Apart from these , urine exam and kidney function tests form part of evaluation. Measuring the urine levels of calcium , oxalate, phosphate , uric acid , citrate is done in individuals with recurrent kidney stones , strong family history of kidney stones.
How to treat kidney stones?
Several measures like drinking plenty of water – about 3-4 litres per day, decreasing the amount of salt and meat in the food , cutting down the amount of tomatoes , spinach form part of treatment for kidney stones. Seeking out the cause of stones and risk factors is an important step in the treatment. Whether to treat the stones by medicines or by surgery depends on the size, content and location of the stone. Stones less than 5mm just get passed along with the urine even without our knowledge. Stones of 5-6 mm get stuck in the ureters (tubes that connect kidneys with urinary bladder ) and cause obstruction to the urinary flow leading to back pressure to the kidney and causing it to swell up. If these stones are not treated , the kidneys are damaged permanently. These stones can be treated medically to some extent. The stones which get stuck in the upper part of the ureters are difficult to come down. Stones of size > 7-10 mm need surgical procedure for their removal.
Various surgical procedures are employed to remove kidney stones.
- Ureteroscopic removal of stones involves inserting an endoscope into the bladder and the ureters via the urethral opening and retrieving the stones under vision. If the stones are big, laser waves are sent to break the stone into small pieces so that these small pieces get flushed out easily. A DJ stent – a string-like an instrument that is placed in the ureter to keep it open for effective drainage of urine along with the debris formed after stone breakage. This is technically referred to as URSL.
- In Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy, high energy shock waves are sent from external source and break up the stone into pieces and these small pieces can easily come out in the urine. It is done under general anesthesia and takes about 45 minutes to 1 hour.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): In this procedure , a long tube is inserted into kidney from the back and stone is removed . Very big stones , cysteine stones , structurally abnormal kidneys need PCNL for stone removal.
How do I prevent kidney stones ?
The best and easy way of preventing kidney stones is taking plenty of water. On an average, a person takes around 2L of water everyday. It is recommended take 3-4 litres of water per day so as to produce 2 litres of urine in people with kidney stones. Avoid food items which are rich in oxalates like tomatoes , spinach , nuts (cashews, almonds, pistachios , peanuts) ,chocolate, beets. People with low levels of calcium in their body are more prone for calcium stones – try to get calcium from natural resources rather than from supplements. Cut down the amount of salt and animal protein in the diet. Avoid junk food , frying , fried food , packaged food so as to avoid increase sodium and phosphorus intake. It is found that the chance of getting a kidney stone the second time is around 20-50% in the lifetime. Thats the reason , stone formers should maintain the above precautions all throughout their lives.